Heating Effect of Current
Joule Heat
When some potential difference V is applied across a resistance R then the work done by the electric field on charge q to flow through the circuit in time t will be 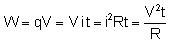 Joule. This work appears as thermal energy in the resistor.
Joule. This work appears as thermal energy in the resistor.
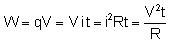 Joule. This work appears as thermal energy in the resistor.
Joule. This work appears as thermal energy in the resistor.Heat produced by the resistance R is 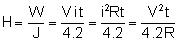 Cal. This relation is called joules heat.
Cal. This relation is called joules heat.
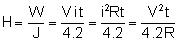 Cal. This relation is called joules heat.
Cal. This relation is called joules heat.Electric Power
The rate at which electrical energy is dissipated into other forms of energy is called electric power i.e.
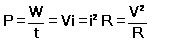
Units: It’s S.I. unit is Joule/sec or Watt
Bigger S.I. units are KW, MW and HP, remember 1 HP = 746 Watt
Rating values
On electrical appliances (Bulbs, Heater, Geyser … etc). Wattage, voltage, … etc. are printed called rating values e.g. If suppose we have a bulb of 40 W, 220 V then rated power (PR) = 40 W while rated voltage (VR) = 220 V.
Resistance of electrical appliance
If variation of resistance with temperature is neglected then resistance of any electrical appliance can be calculated by rated power and rated voltage i.e. by using 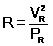
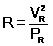
Power consumed (illumination)
An electrical appliance (Bulb, heater, … etc.) consume rated power (PR) only if applied voltage (VA) is equal to rated voltage (VR) i.e. If VA = VR
So Pconsumed = PR. If VA < VR then Pconsumed = VzA/R also we have R = VzR/PR
So Pconsumed (Brightness) = (V2a/V2R) × PR
Long distance power transmission
When power is transmitted through a power line of resistance R, power-loss will be i2R
Now if the power P is transmitted at voltage V then P = Vi , i.e. i = (P / V)
So Power loss = P2/V2 × R
Now as for a given power and line, P and R are constant so Power loss ∝ (1/V2)
So if power is transmitted at high voltage, power loss will be small and vice-versa. This is why long distance power transmission is carried out at high voltage.
Electricity Consumption
1. The price of electricity consumed is calculated on the basis of electrical energy and not on the basis of electrical power.
2. The unit Joule for energy is very small hence a big practical unit is considered known as kilowatt hour (KWH) or board of trade unit (B.T.U.) or simple unit.
3. 1 KWH or 1 units is the quantity of electrical energy which dissipates in one hour in an electrical circuit when the electrical power in the circuit is 1 KW thus 1KWH = 1000W × 3600 sec = 3.6 × 106 J.
4. Important formulae to calculate the no. of consumed units is
n = Total Watt × Total Hours/1000
Solved example 1: Two heater wires of equal length are first connected in series and then in parallel. The ratio of heat produced in the two cases is
(A) 2 : 1 (B) 1 : 2 (C) 4 : 1 (D) 1 : 4
Solution: (D) Power consumed means heat produced.
For constant potential difference Pconsumed = Heat ∝ 1/Req
H1/Hz = Rz/R1 = R/2/2R = 1/4 (Since Rz = R.R./R+R = R/2 and R1 = R + R = 2R)
Solved example 2: A wire when connected to 220 V mains supply has power dissipation P1. Now the wire is cut into two equal pieces which are connected in parallel to the same supply. Power dissipation in this case is P2. Then P2 : P1 is
(A) 1 (B) 4 (C) 2 (D) 3
Solution: (B) When wire is cut into two equal parts then power dissipated by each part is 2P1
So their parallel combination will dissipate power
P2 = 2P1 + 2P1 = 4P1, Which gives P2/P1 = 4.






1 comments:
Really nice work for student !
To get more questions, you can also consider using website www.jsuniltutorial.weebly.com
Post a Comment