Combination of Bulbs
Bulbs in Series
(i) Total power consumed 1/Ptotal = 1/P1 + 1/P2 +...
(ii) If ‘n’ bulbs are identical, Ptotal = P/N
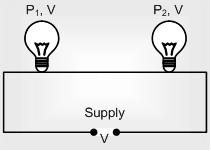
(iii) Pconsumed (Brightness) ∝ V ∝ R ∝ 1/Prated i.e. in series combination bulb of lesser wattage will give more bright light and p.d. appeared across it will be more.
Bulbs in Parallel
(i) Total power consumed
Ptotal = P1 + P2 + P3 +...+ Pn
(ii) If ‘n’ identical bulbs are in parallel Ptotal = nP
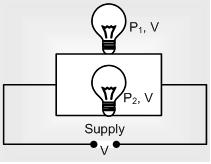
(iii) Pconsumed (Brightness) ∝ PR ∝ i ∝ 1/R i.e. in parallel combination, bulb of greater wattage will give more bright light and more current will pass through it.
Solved example 1: An electric bulb is rated 220 volt and 100 watt. Power consumed by it when operated on 110 volt is
(A) 50 watt (B) 75 watt (C) 90 watt (D) 25 watt
Solution: (D) Resistance of the bulb V2/PRotate = 220×220/100 = 484 Ω
When connected with 110 V, the power consumed
Pconsumed = V2/R = 110×110/484 = 25W
Solved example 2: Two bulbs are working in parallel order. Bulb A is brighter than bulb B. If RAB are their resistance respectively then and R
(A) RA > RB (B) RA < RB
(C) RA = RB (D) None of these
Solution: (B) In parallel Pconsumed ∝ Brightness ∝ 1/R
PA > PB (given). RA < RB






0 comments:
Post a Comment